How to Develop a Successful Marketing Automation Strategy
As the number of Internet users increases, companies try harder to stay on view. They launch more online ads, try to be present on all social media platforms, and strive to collect Big Data about markets and leads. As a result, work by hand is no longer enough. More and more businesses switch to semi- or fully automated marketing processes. So, the market for digital marketing software is flourishing, with an average annual growth rate of 18.2% by 2028. In this article, we’re going to guide you through the main principles of building a successful marketing automation strategy and helpful software toolkit.
What is a Marketing Automation Strategy?
Marketing automation is a process of streamlining lead generation and nurturing, up to the closed deal, with minor manual works. Its goal is to make all marketing activities, whether they are standalone advertising campaigns or multi-channel targeting, self-regulated, and value-for-price. As a result, marketing ROI increases, and a company gets many side economic and operational benefits.
Like any business activity, marketing automation involves people, processes, and tools. It requires investments, and so it is expected that actions will bring apparent returns, e.g. increased website traffic or a higher % of conversions. For these to happen, automated actions shall be planned, aligned, prepared, and appraised. In other terms, a marketing automation strategy shall be developed.
Automation starts with laying these out:
Growth Strategy
The ultimate business aim is revenue increase, however, this may be achieved through different approaches. For example, if a company chooses to be a leader in audience reach, it may need to utilize different communication channels – to address many user segments. Even though the conversion ratio may be low, the company will earn more because the funnel’s TOFU layer will be better filled. On the contrary, a business may choose to become more specific in targeting and focus on increasing the % of closed deals. Both cases will require distinct approaches to automation, agree.
Target Audiences
Before purchasing a software license, one needs to know customers. In particular – what unsatisfied needs they may have, what communication channel they prefer, what social platforms they use, what’s the right time to reach out, what content may capture attention, and so on. A good idea is to build Buyer persona profiles so that clients will no longer be abstract segments for targeting.
Customer Journeys
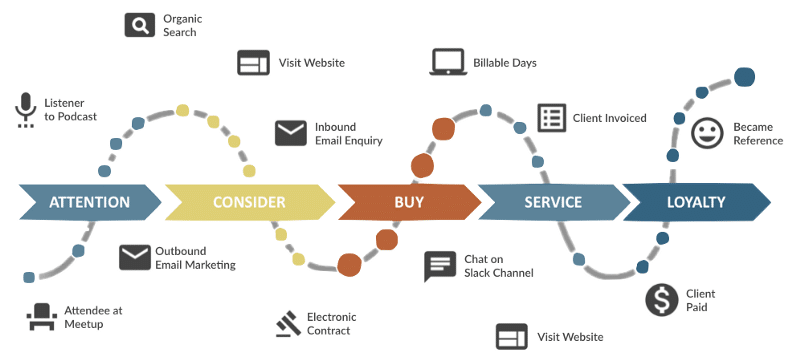
“Customer journey map helps to place communication channels in some kind of order”, Image Source
The last point is to understand how people receive information about the brand and what stages they pass through before making a purchase. If you run digital marketing campaigns and keep information about their performance, you may do marketing attribution. It will reveal what touchpoints have principally contributed to conversions and give an idea of how to start the automation.
If a company develops all marketing processes from scratch, it can map out several customer journeys. After the automation is launched, the company can test initial hypotheses and find out what journey “route” leads to conversions.
Resources
Implementing automation can cost from several tens to several thousands of dollars, and even more. A software subscription alone isn’t that expensive – you can pay around $45 per user per month for a quite good set of features. Plus, there are many free tools, e.g. CRMs, CMS’s, email schedulers, and so on.
However, in case your team consists of dozens of employees, or you want to access advanced settings, automation tools may cost a penny. Not to say one may need to hire digital marketers who will set up everything.
Competitors’ Actions
It’s not only about what the company wants or can implement – but the automation strategy depends also on what practices are common on the market. Of course, every company has its unique strategy, but it may be worth extracting certain patterns. For example, wordings that competitors use in newsletters, media they publish at, lead magnets they use, articles they post in blogs, and so on.
Finally, the company can proceed to implement the automation strategy.
Building Processes
Although modern software uses machine learning and is enhanced with AI technologies, it can’t operate without an algorithm. To launch automation, a company has to work out inner procedures and documentation. Employees shall understand how the information flows between Sales, Marketing, and Management – who’s in charge of viewing and editing it, what templates to use under certain conditions, and how much time is allocated for different marketing activities. The more well-thought operations are, the better automation outcomes will be.
Hiring & Training Employees
To make the most of automation software, employees shall understand the full range of opportunities they can use. For example, to become proficient with an analytics pack from Google, one has to complete 6 different courses in an Academy. So, make sure you not only invest in programs, but also in people who will use them.
Performance Assessment
Marketing automation is much about KPIs. One can read about many “cost per” or “returns on” metrics, such as CTR, CPI, CPC, CPA, and more. Your aim should be to determine what can describe campaigns’ performance better. And what’s even more important – what KPIs will help you to improve digital marketing activities in the future.
Developing a Successful Marketing Automation Strategy
Understanding where to use automation
You can use automation all over the customer journey stages:
1. Awareness
Automate Inbound and Outbound marketing. You can naturally attract leads through content marketing and SEO, for example, by ranking for specific keywords in the Google search engine, publishing capturing content, filming tutorials, and so on. For Inbound activities, try these tools:
- Similarweb, SEMrush, or Ahrefs – to collect insights about keywords, topics, and competitors across countries; these tools have APIs, so you can automate data collection
- Google Analytics and Search console – to collect and analyze website traffic, keywords, positions, audiences, track conversions, compare and improve landing pages.
As for Outbound marketing, paid lead gen campaigns may be the only source for short-term website traffic or customer flow, especially for newly established companies. To run them, use:
- Facebook, YouTube, Twitter Ads – to set up and monitor campaigns
- LinkedIn Sales Navigator – to find prospects on B2B
- Google Search, Display, Video, Shopping, and other types of ads campaigns – to purchase traffic via Google.
2. Research
You have to know where your prospects look for information. And – be there with relevant content and on time. Some helpful marketing tools for that:
- HubSpot – to schedule and publish to your Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other networks
- Zoho Social – to manage profiles on multiple social media platforms; allows to plan, schedule, and track content performance
- SlideShare – to create presentations and after – embed them into blog posts and websites, or share via socials.
3. Consideration and Conversion
The person may hear about your brand from multiple sources before deciding to purchase what you offer. As such, you have to run multi-channel campaigns. Try these omnichannel campaign management tools:
- Adobe Experience Cloud – to plan and execute marketing activities across channels (direct mail, email campaigns, SMS and push notifications, and others)
- ActiveCampaign – to automate email marketing and sales
- Snov.io, Sendinblue, MailChimp, GetResponse, and other email automation tools – to build email sequences, personalize email content, and work with analytics.
4. Loyalty
Customer experience is of TOP importance for companies. To automate support and work with leads, try the following instruments:
- CRMs – to keep and use information about previous offers, deals, dialogues’ history, and so on
- EngageBay – to automate ticket processing and routine customer service processes.
Establish benchmarks
Essential prerequisites for successful marketing automation are templates. These allow to transfer and scale experience. If you still don’t have benchmarks, start with the following:
- Email and direct messages templates – you need to create sample adjustable subject lines and copies for all occasions: cold outreach, to welcome new subscribers, to offer a deal, for regular newsletters, and so on
- Drip campaign examples – email sequences upon users’ actions are higher open ratios than stand-alone emails; depending on your business type, you may need templates for the following campaigns: to verify new email address, to promote a new product or service, to collect feedback, to increase user engagement, to remind on the upcoming event
“Drip emails allow to achieve better content personalization and target leads more precisely”, image source
- Business offer templates – create standard forms for solicited and unsolicited proposals that marketers and salespeople can further personalize and re-send to clients.
Research and Development
A successful automation strategy is a flexible one. Consumers’ preferences, interests, and concerns change over time, and so should your marketing activities. You can:
- Monitor Google Trends and check up what people search for in your region or country
track & analyze social media mentions of your or competitors’ brands and make informed decisions about further promotion - Collect feedback from customers or launching a poll survey
- Collect advanced website analytics, for example, via monitoring heat maps
- Keep an eye on competitors’ marketing activities.
Lead nurturing
People do want to receive personalized and relevant messages. As such, an effective automation strategy is impossible without custom content paths for every single lead. Your lead nurturing shall start with segmentation and result in distinct campaigns’ content. Make sure to do some preps before implementing automation itself:
- Identify target audiences – work out key accounts or Buyer personas profiles
- Work out scouring system or criteria – to determine qualified leads
- Perform initial segmentation
- Identify points of contact with every segment
- Work out a content strategy about segments, including ads messages and visuals
- A\B test ad campaigns – to see what combinations of content and creatives perform better for every segment
- Review segments and adjust them according to clients’ behavior, e.g. the level of engagement, loyalty grade, etc.
Benefits of Using an Effective Marketing Automation Strategy
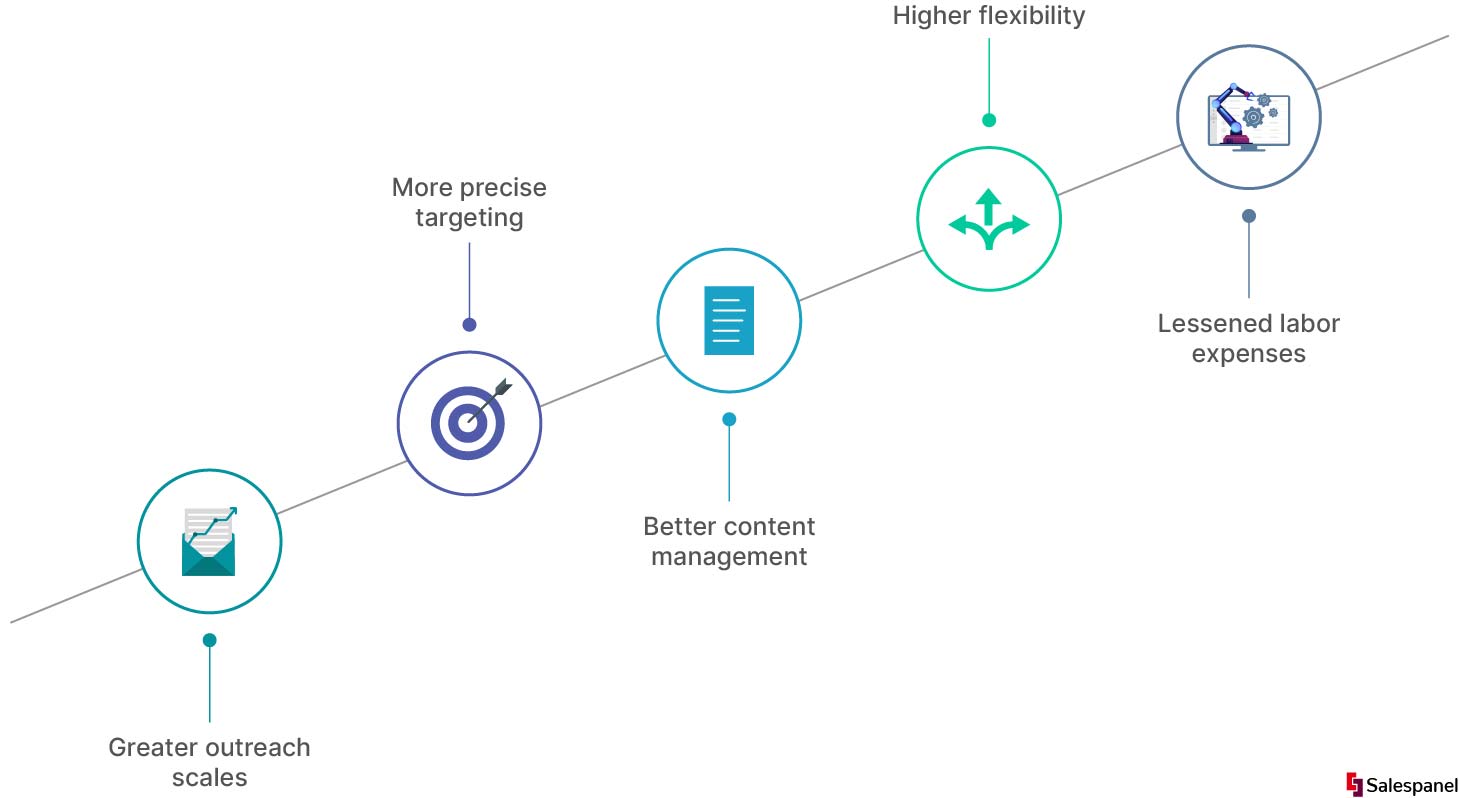
If you manage to overcome obstacles to marketing automation, be prepared to experience the following advantages:
Greater outreach scales
There are many kinds of marketing automation tools, and a distinct chunk of these are aimed to automate outreach. If one sends several dozens of emails per day it may not be a matter for automation, but when it comes to several hundred – mere teams can perform mailings manually and keep it effective, agree.
Not only automation allows to address more leads – it helps companies doing it safely. For example, with regulated trigger-based email campaigns, a company eliminates the risk of being accused of spam. Moreover, automated marketing systems lead to improved KPIs, such as the number of successfully delivered emails or open ratio.
More precise targeting
Marketing automation starts with audience segmentation. In doing so a company may group leads according to as many parameters as needed because it is an algorithm that does all targeting jobs. For example, Facebook Ads Manager allows creating custom audiences upon not only users’ location or demographics, but also with taking into account their interests, actions, and connections.
A segment may include as few as 2 or 3 people if you believe it is relevant for targeting goals. After segmentation, every group is addressed with a distinct “pack” of ad components – messages, CTAs, and ad creatives.
Better content management
Content production and distribution may be a tough job if done 100% by hand. The amount of content an average company should handle daily is quite substantial: regular newsletters, follow-ups, social media posts, blog publications, messages in ads, etc. Not to mention dialogues with prospects or clients via phones or messengers. Content management systems help to keep everything running. They store content, publish or send it according to the schedule, track user engagement, collect analytics, and allow marketers to collaborate better.
Higher flexibility
Consumer behavior and reactions aren’t a given – their needs, interests, and preferences change over time. As so should your digital marketing strategy. Self-regulated marketing activities help a company stay agile. For example, programmatic – an automated selling and buying of advertising – presumes real-time bidding for showing ads impressions. Within fractions of a second AdExchange compares bidders’ prices, audience’s parameters, and assess message’s parameters. Thus, marketers can track how much they spend and what users do they target in real-time. And – adjust campaigns, if required.
Lessened labor expenses
Automation reduces the need for manual work. No longer do marketers have to spend time assembling and skimming through Excel tables or following up with clients. Moreover, they can act more productively by using common best practices, e.g. email drip campaign examples or newsletter templates. As a result, a single employee can work everything that 2 or 3 marketers were previously involved in. For an employer, this means – significant savings on wages.
Marketing automation can shorten sales cycles and bring more qualified leads to the funnel. If handled strategically, it allows companies to engage more prospects, cut operational expenses, and work with comprehensive analytics.
Sell more, understand your customers’ journey for free!
Sales and Marketing teams spend millions of dollars to bring visitors to your website. But do you track your customer’s journey? Do you know who buys and why?
Around 8% of your website traffic will sign up on your lead forms. What happens to the other 92% of your traffic? Can you identify your visiting accounts? Can you engage and retarget your qualified visitors even if they are not identified?


