What is a Good CPM? Understanding CPM for B2B
Updated on 25th May, 2024
Advertisements are the most direct way of marketing your brand, product, or services. It is what delivers your marketing content to your audience through various channels at a very large scale and in a relatively short time.
In the earlier days, pricing for advertisements was a relatively easy affair. For print media, it was the page and size of adverts and for televisions and radios, it was the duration and time slots that decided the cost for advertising.
However, advertisement on the internet works differently, and the traditional measures that decide the cost of advertisements do not work here. What we have for the digital space is “impressions”, i.e., the number of times an advert is loaded onto a webpage. So how exactly does the pricing for advertisements work using ‘Impressions’ as a measure?
The most widely used method is CPM, i.e. Cost Per Mille (Mille is derived from Latin, meaning a “thousand”).

Image Courtesy – madgicx.com
Let Us Understand CPM Properly
Before we dive into what can be considered a “good CPM”, let us understand what CPM is. Cost per mille (thousand) is the most widely used metric for pricing web advertisements in Marketing. The main component of this metric is impressions, which is the count of digital views or the count of times an advertisement was loaded on a webpage.
Other metrics like Cost Per Click are also used for pricing web adverts but by far the majority of the top advertising platforms primarily use CPM for display advert pricing.

Image Courtesy – theonlineadvertisingguide.com
Based on the CPM model, the advertiser agrees to pay the advertising platform or website a set fee for every 1000 times their advertisement is viewed or is loaded along with the webpage in the browser window.
Thus, if the advertisement rate of a website or advertisement platform is $3 CPM, that means they’re charging you $3 for every 1000 times your advert will be viewed or loaded on their webpage or platform.
What is a Good CPM in B2B?
This is a difficult question to answer and most experienced marketers in the B2B space will tell you that a good CPM is subjective and highly depends on the objectives of the advertisement campaign and the advertisement platform.
For instance, Let’s consider that for an advertisement platform the average CPM for B2B is $4. If you land a deal for a CPM of $3.50 and you achieve the objectives of the advertisement campaign, the CPM can be said to be good.
In case you landed a deal for a CPM of $6 and did accomplish the objectives of the advertisement campaign then, despite paying above the industry average, your CPM can be considered to be a good one.
Therefore, the crux of the matter is that a low CPM is not always good. As long as the objectives of the advertisement campaign are being met and the CPM is within reasonable limits of the industry average, the CPM can be considered as good.
Facebook is considered the best B2B advertising platform and as per the latest figures, the average Cost per mille stands at $22.50. So, for Facebook B2B advertising, a CPM within reasonable limits of $22.50 that achieves all the objectives of your advertisement campaigns will be considered a good CPM.
Typical CPM for Google
Google has the largest market share among search engines, which makes it one of the most popular places to advertise. According to Semrush, the average CPC in Google Ads across industries is $2.69 for Search and $0.63 for Display.
Google allows you to set a daily budget, just like any other advertising platform. This way, you don’t have to worry about your CPM or click-through rates skyrocketing. Your ad would automatically go dark once it receives the number of clicks that are allowed based on the budget you have set, keeping your ad expenses in check.
How To Maximize Your Google Ad Spend?
To maximize your Google Ad spend effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Set Clear Objectives: Define specific goals for your campaigns to guide your strategy and measure success accurately.
- Performance Planner: Use Google’s performance planner to forecast potential outcomes and optimize your budget allocation.
- Keyword Targeting: Focus on high-performing, relevant keywords, and create specific, targeted ad groups.
- Adjust Bids: Regularly review and adjust your bids based on performance data to ensure optimal spending.
- Ad Extensions: Utilize ad extensions to increase visibility and click-through rates.
- Conversion Tracking: Implement conversion tracking to measure the success of your campaigns and make informed adjustments.
- Optimize Landing Pages: Ensure your landing pages are relevant and provide a good user experience to increase conversions and reduce bounce rates.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor and refine your strategy to improve return on investment.
Many companies today spend a significant amount of money on social media advertising, even though CPMs can differ significantly amongst social media platforms. Twitter offers the lowest CPM at $5.76. For Instagram advertisements, the average cost is $6.70, while LinkedIn ads cost $6.05 on average. Facebook can be the most expensive with a price of $9.06.
However, Facebook offers far lower click-through rates, so the compromise might be worthwhile. Compared to $0.53 on Twitter, $1.28 on Instagram, and an astounding $5.61 on LinkedIn, Facebook’s CPC is only $0.51 on average. LinkedIn’s high CPC can be explained by its extremely niche B2B customers.
Understanding which platform your own potential customers are most likely to be using is a crucial component of obtaining the highest CPM value. Adults spend most of their time on Facebook and YouTube together. The market shares of other social media sites are substantially lower. These include Instagram, Pinterest, Snapchat, LinkedIn, Twitter, and WhatsApp, in that order of predominance.
However, you should be aware of the social media channels that members of your own target audience are using, in case your business targets very specific demographics. While YouTube and Facebook are used by adults between the ages of 18 and 29, people from younger age groups—especially those between the ages of 18 and 24—use Instagram and Snapchat far more frequently. Besides this, a much higher proportion of women than men use Pinterest.
For instance, if you have determined that Facebook is the most appropriate social media network for your advertising budget, you can create specialized audiences using the Facebook Audience Manager tool, to maintain a low CPM rate. Users can be targeted according to their location, interests, behavior, demographics, app usage, and more. Additionally, Facebook offers a feature called “lookalike audiences” that enables you to target your ads to users that are similar to your current target prospect population.
On the other hand, if Twitter is your preferred platform, you may tailor your adverts according to demographics like age or gender, interests, and other brands they follow in addition to your own CRM data. You can further target members of LinkedIn based on their industry, job title, company name, or professional interests. Finally, to target Instagram audiences, you can use options such as demographics, hobbies, and behaviors in addition to geography. Instagram also allows you to create lookalike audiences, similar to Facebook.
CPM v/s Other Advertisement Metrics
There are some inherent problems with CPM as a metric for advertisement which has led to wide usage of other metrics. These are:
Cost per Click (CPC)
Cost per Click is the average price you pay every time a viewer clicks on the link in your ad and lands on your website. Unlike CPM, you are paying for the actual interaction a viewer has with your ad in the case of CPC.
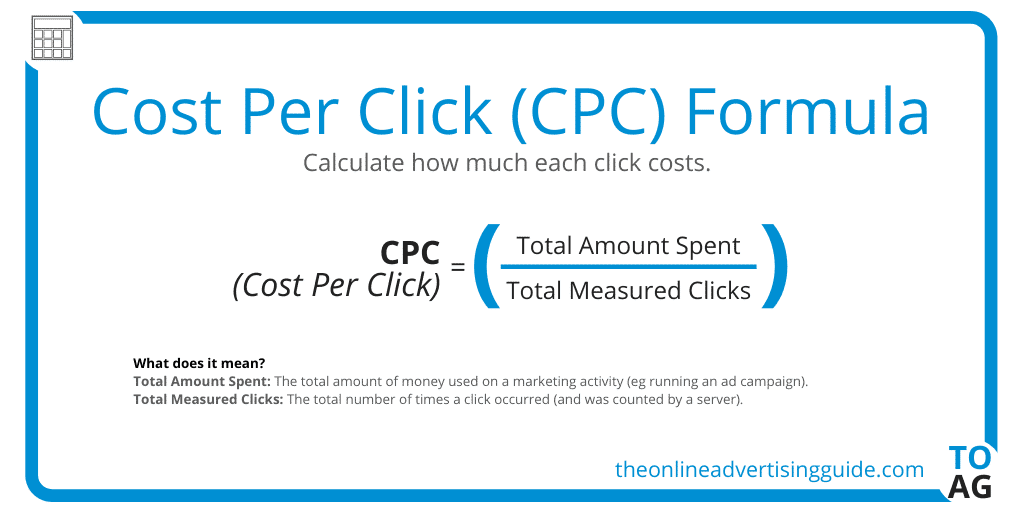
Image Courtesy – theonlineadvertisingguide.com
Using the Cost per Click model is the best way of driving traffic to your website as you are only paying for people who actually land on your site and not just for impressions. Results for CPC are very easy to track and understand compared to CPM. It also gives more ease of mind to advertisers as you only pay for what you get.
Cost per Engagement (CPE)
Cost per Engagement is the average price you pay every time a viewer interacts with your advert. The interaction may be in the form of clicking a link in your ad, liking your post, sharing it, or commenting on it.
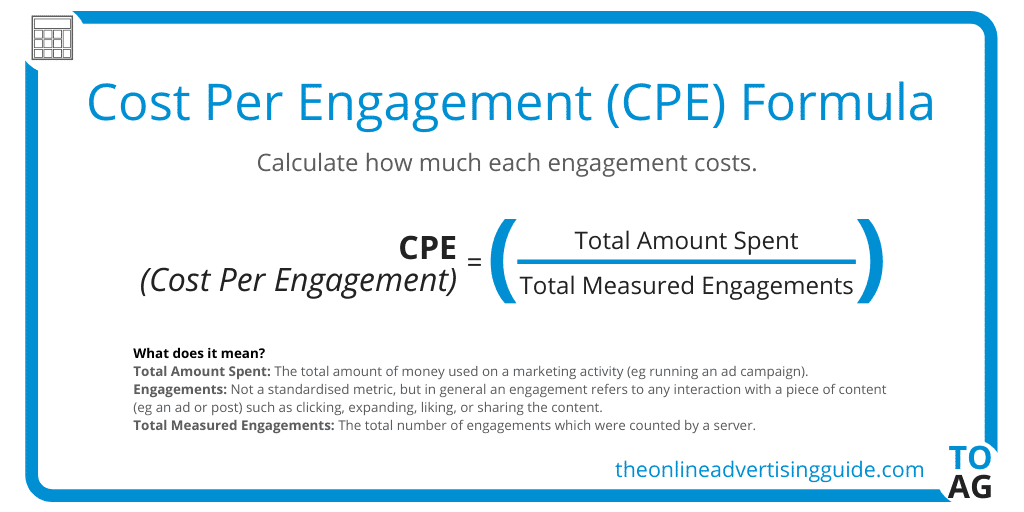
Image Courtesy – theonlineadvertisingguide.com
CPE is a good metric for two things. First, its performance is visible in the form of post likes, comments, and shares, and second, these interactions raise the engagement of a post which in turn makes most social media platform algorithms boost the reach of these posts, earning you more organic reach. Plus, its visible to other people you reach as “validation”.
Imagine seeing a sponsored post on your feed that links to an article. This post has no likes, comments, or shares. On the other side, imagine seeing the same post with several likes, shares, and comments. Which one are you more likely to click?
Cost per Engagement is better for advertisers who are trying to boost the overall engagement of adverts on social media.
Cost per 1000 Reached
Cost per 1000 Reached is the average price you pay to have your advertisement placed in front of 1000 people. How does it differ from CRM? Cost per 1000 Reached only counts unique impressions, whereas CPM counts all impressions.
This metric is a better choice than CPM if you are planning to run an awareness campaign which reaches as many people as possible. Cost per 1000 Reached This metric shows you how many actual viewers saw your ad and not how many times your ad was displayed.
Top Benefits of CPM as an Advertising Metric
Here is why you should choose CPM as your advertising metric to analyze ad performance:
- Broad Reach: CPM allows advertisers to reach a large audience, making it ideal for brand awareness campaigns aiming to maximize visibility.
- Budget Control: With CPM, advertisers know the cost upfront, making it easier to plan and manage budgets effectively.
- Comparative Analysis: CPM facilitates easy comparison of the cost-effectiveness of various advertising channels and formats.
- Scalability: CPM-based campaigns can be easily scaled up to increase reach without significant changes to the pricing structure, supporting large-scale advertising efforts.
- Simplicity and Transparency: CPM is straightforward, providing a clear metric for evaluating the cost of ad exposure across multiple different advertising platforms.
Factors that affect CPM
There are varying factors that determine the CPM value. Some can be tweaked and controlled while some cannot be. Below we have listed down some notable determinants that affect the CPM value. These include:
Geography
The CPM value typically depends upon how developed the online and digital space is in a region or country and the per capita purchasing power of the inhabitants of that region or country.
For instance, the CPM values are higher in Northern Americas and Europe compared to Asia and South America.
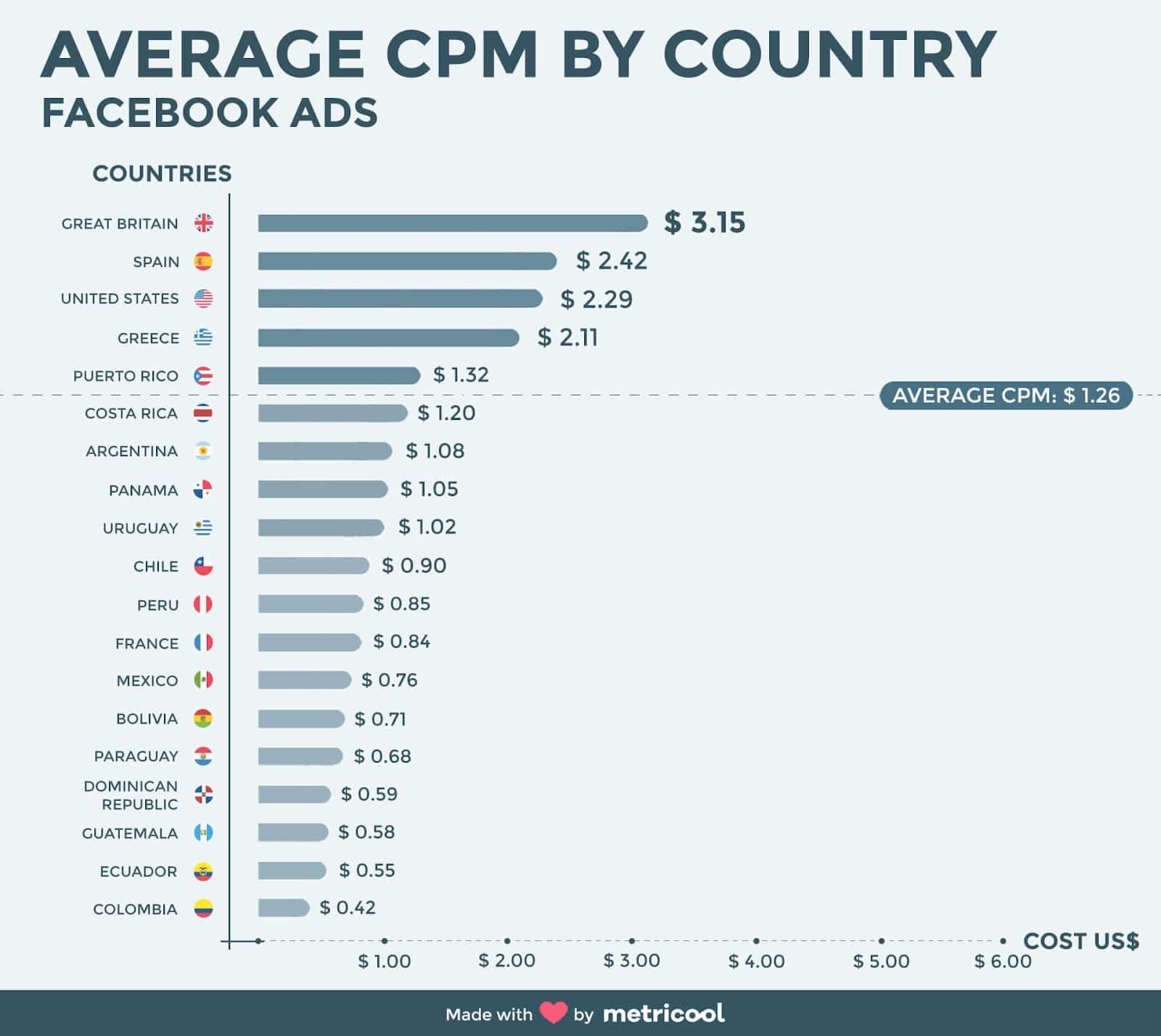
Image Courtesy – metricool.com
Ad Format
The CPM value also depends on the format in which you are advertising. For instance, the CPM value for a video advert will be more than that for a static image advert.

Image Courtesy – madgicx.com
Ad Size
The space you require to put up your advert on a website or a webpage will affect your CPM value. This is because CPM value is directly proportional to the size of your advert in terms of webpage space it shall occupy.
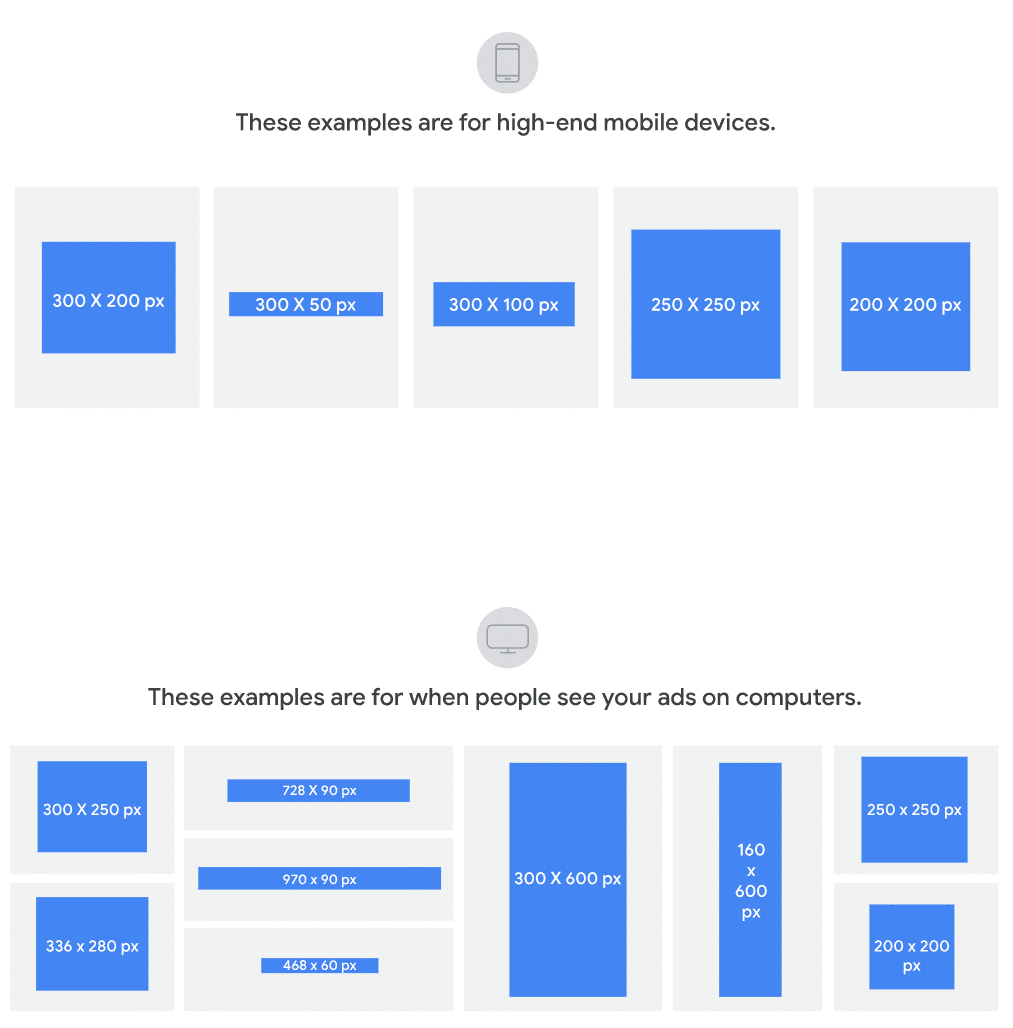
Image Courtesy – google.com
Seasonality
Web traffic fluctuates a lot from season to season and so do spending habits. The CPM values are usually high during the holiday season when people are looking to spend on gifts to buy things for festivities. Seasonality differs from region to region.
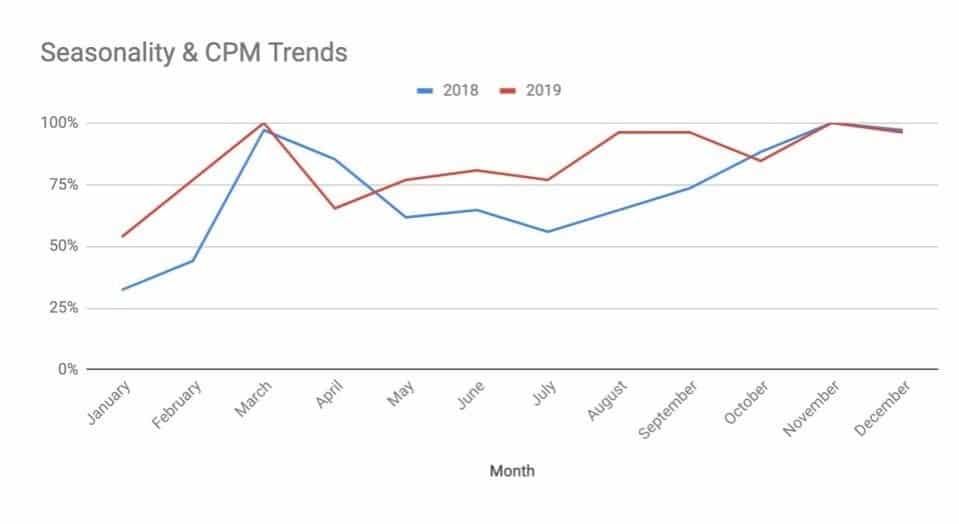
Image Courtesy – dapex.io
Market Demand for Your Set of Audience
CPM values tend to be affected by the market demand for the particular set of audiences you target with your ads. This is because market demand for a particular set of audiences is directly proportional to the CPM value.
The more competitors you have bidding for the placement, the more price you will pay.
Number of Ads on a Webpage
This is a classical case of supply and demand. Demand being constant, additional advert slots on a web page will drive down the value of CPM.
Device
Mobile-only adverts typically have a lower CPM compared to desktops owing to the screen size, resolution limitation, lower CTR, and conversion rate. This is changing for B2C however, as most B2C users on platforms like social media are on mobile. B2B users, on the other hand, are more likely to take action on desktop.
Optimizing CPM for Advertising
Knowing what factors affect the value of CPM helps advertisers devise ways of optimizing its value to a level that suits their budgets while still accomplishing campaign objectives. Some effective ways of optimizing CPM for advertising are:
Targeting the Right Audience
Reaching the people who may be interested in your brand has two positive effects. One, you are spending effectively by reaching the right people, and two, reaching the right people raises your advert’s relevance score, which in turn lowers your CPM.
Not Opting for an Overly Specific Target Audience
Opting for an overly-specific set of audiences results in excess demand over the supply which raises the CPM as a result. The key here is to be specific but not to an extent that leads to a situation of excess demand for a specific audience over its supply. Plus, a very small audience might not get the number of impressions you want.
Improving the Relevance Score of Your Ad
Advertisement platforms should take note of how relevant their ads are to the audience and score them accordingly. Improving the ad relevance score has many benefits. In this case, ads with higher relevance scores are boosted in terms of reach by most advertisement platforms’ algorithms which results in a lower effective CPM. Highly relevant copywriting along with the content displayed once visitors get to your website should increase the relevance scores. Factors like page load speed and overall user experience also contribute to this.
Create Engaging Ads
Creating catchy adverts is very important as most of the people on the internet are used to scrolling past or ignoring irrelevant and lackluster ads. Creating a standout ad has two benefits, firstly your audience will pay attention to it and most likely will share it, and secondly, it will boost the engagement rate which in turn results in lower CPM for you.
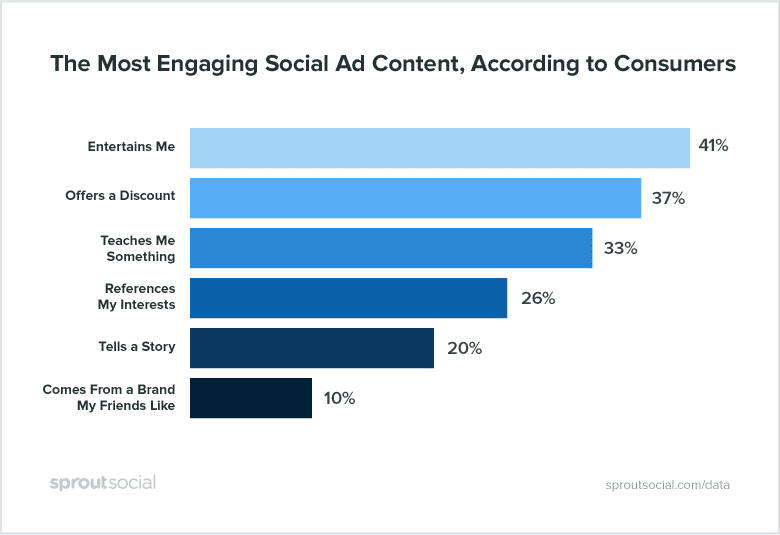
Image Courtesy – Sprout Social
A/B Testing
Split testing your advertisements in terms of audience, ad content, CTA, ad formats, etc. will enable you to understand what’s working and what’s not. With this knowledge, you can create ads that generate higher relevance scores, engagement and shares which result in directly or indirectly lowering your CPM.
Image Courtesy – Hallam Internet
Selecting the Right Ad Format
Yes, video ads are more effective but do you need one? Knowing what message you need to deliver is important as it will help you choose the right ad format. If you need to deliver a short message, an image ad will be sufficient for it. Images often have lower CPM rates due to simpler, faster consumption, making them cost-effective for campaigns needing broad reach without the higher costs associated with video production and delivery.
Ad Timing and Frequency
Deciding when to show your ad and how many times to show it are important decisions. As mentioned earlier, engagement and relevance are two important determinants of CPM.
Right ad timing and frequency will help you raise engagement and relevance score and in turn, those two will help lower your CPM.
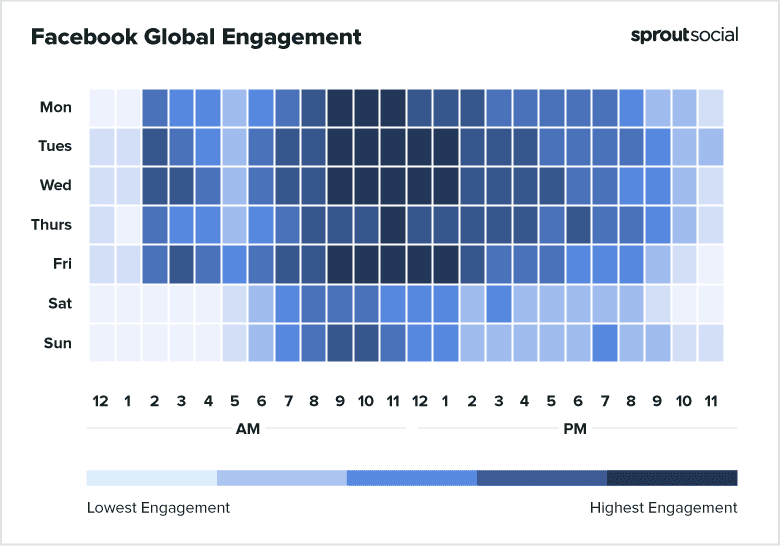
Image Courtesy – Sprout Social
Wrapping it Up
While there are marketers out there who say that CPM is an obsolete advertising metric, CPM is still relevant and widely used. This is because other metrics serve specific roles for the completion of specific advertisement campaign objectives .
CPM is still the most generalized, all-inclusive Advertisement Metric. Understanding what a good CPM is, what all factors affect it, and how it can be optimized is crucial for young Marketers and offers a significant competitive advantage to them.
Sell more, understand your customers’ journey for free!
Sales and Marketing teams spend millions of dollars to bring visitors to your website. But do you track your customer’s journey? Do you know who buys and why?
Around 8% of your website traffic will sign up on your lead forms. What happens to the other 92% of your traffic? Can you identify your visiting accounts? Can you engage and retarget your qualified visitors even if they are not identified?


