Lead Qualification 101: What is a Qualified Lead?
The B2B sales process involves multiple steps. Lead qualification is one of the crucial ones.
Leads are prospects that a business hopes to turn into paying customers. It takes considerable effort on the part of marketing and sales teams to convert leads. Only a small fraction ends up as customers. The problem here is that with digital marketing making products more accessible globally in the self-service model, businesses come across more unqualified leads. Resources now need to be carefully utilized and spent on the right prospects.
Lead qualification comes in to understand the strategies and techniques needed to identify the best sales targets amongst a wider pool of prospective clients. When done effectively, it creates a more streamlined sales process and delivers better conversion rates. As marketing and sales teams improve their ability to identify the best prospects, they can prioritize their efforts better and limit time wastage on leads that are less likely to convert. Let’s better define what lead qualification involves and how to develop an effective lead qualification process that best suits your business.
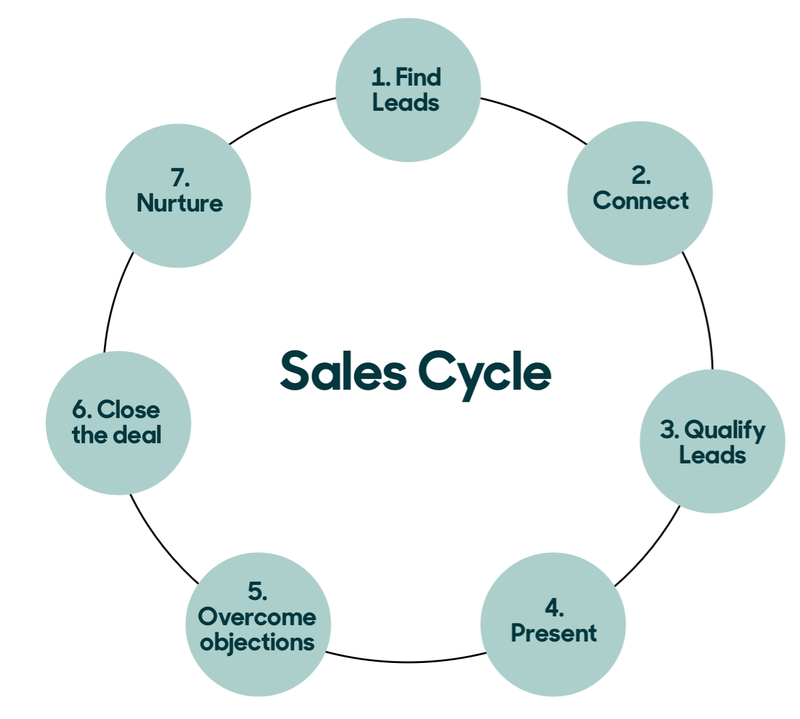
Image Source: fool.com
What Is Lead Qualification?
Lead qualification involves filtering through your existing leads to identify those that match your ideal customer profile and are likely to become paying customers.
These leads may have already engaged with your sales team and read marketing content, and are further along the sales funnel than other leads.
The lead qualification process involves several steps. The marketing team first collects leads and their information. They then try to determine if the lead matches any of their ICPs or if the lead performs favorable actions.
For example, Salespanel users often use key page visits as an important metric for qualification. If there is a match, then the lead qualifies and is pushed through to the next step along the funnel towards sales.
The sales team receives the prospect’s details and makes contact. This is often in the form of a call. They try to find out more about the client’s needs, purchasing power, budget, authority to make purchasing decisions, and timeline. Discovery calls are frequently used by sales teams to determine if a lead is ready to pursue for sales.
What Is a Sales Qualified Lead?
A sales qualified lead is the prospect evaluated by the sales team and found to have the strongest chances of converting. It may not mean they will immediately make a purchase, but rather they have the ability, authority, and intention.
Leads that are often discarded at this stage are unqualified for several reasons. They may not yet be ready to make any purchase. They may not also be financially able to afford your price range or are not sure your product is what they need.
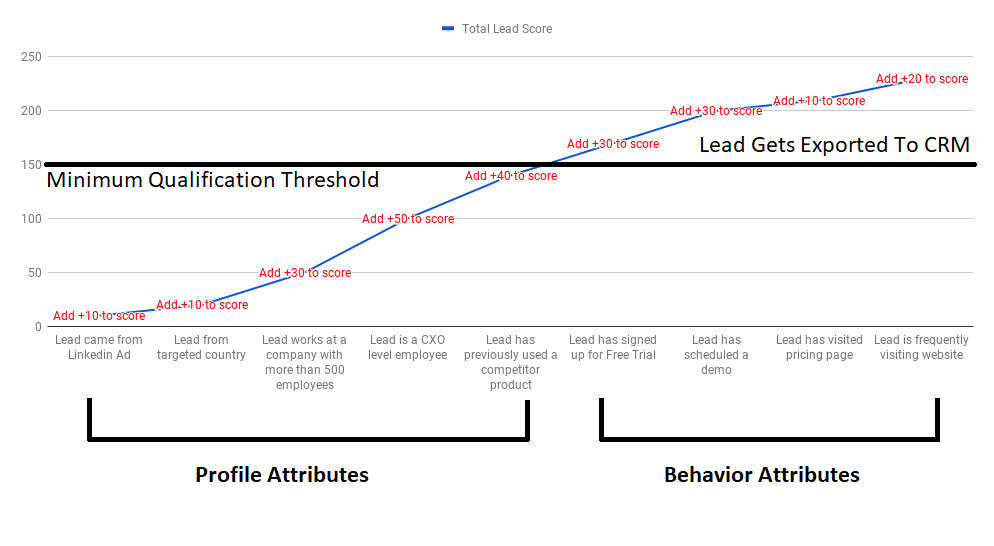
For sales teams to more accurately evaluate leads, a scoring model is needed. This provides a quantitative and data-driven process by which to arrive at the best prospects. It involves identifying factors against which to score each lead. Here are some of the most commonly used lead qualification techniques and the factors they focus on to help narrow down to top contenders.
What Necessitates Proper Lead Qualification for B2B Businesses?
Lead qualification is the cornerstone of B2B sales success. It’s the discerning eye that separates the wheat from the chaff. It ensures sales teams dedicate their resources towards leads with the highest chances of conversion.
Take lead qualification away and your sales team will pursue any and every lead. The result? Chaos in terms of clarity, revenue growth, and projections.
Think of it as a high-stakes game of poker: Every chip (time, money, human capital) is valuable. You wouldn’t bet your entire stack on a weak hand, would you? Likewise, you shouldn’t invest heavily in pursuing a lead that shows little promise.
So how do the winnings look?
1. Increased Sales Efficiency: By focusing sales efforts on qualified leads, sales teams can maximize deal closures and boost revenue growth.
2. Improved Sales Accuracy: A clear understanding of lead fit and buying stage allows sales reps to tailor their pitches effectively. Thus increasing the likelihood of closing deals and reducing wasted effort.
3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: When an ideal and purchase-ready lead becomes a customer, their needs are satisfied to the fullest and swiftly. This leads to a higher degree of customer satisfaction.
How Does Lead Qualification Work?
Marketing Qualification
Considering that we are a marketing-focused blog, we have talked about marketing qualification in detail multiple times. To sum up, marketing qualification relies on ICP matching (profile and firmographic data) and behavioral intent matching (web activities, email engagement, etc.). Marketers use segmentation and lead scoring techniques to use these data attributes and generate marketing qualified leads.
In this article, we will look at sales lead qualification, but if you want to know more about marketing qualification, please check out these articles we have previously written:
Lead Qualification: Drive Conversion on Scale With an Automated Processing Engine
Sales Qualification
When sales teams reach out to leads forwarded to them by marketing teams, they get in touch with each one to try and collect more information. This data then goes into further evaluating their prospects of becoming long-term paying customers. Sales teams may use different types of frameworks to decide what information to collect.
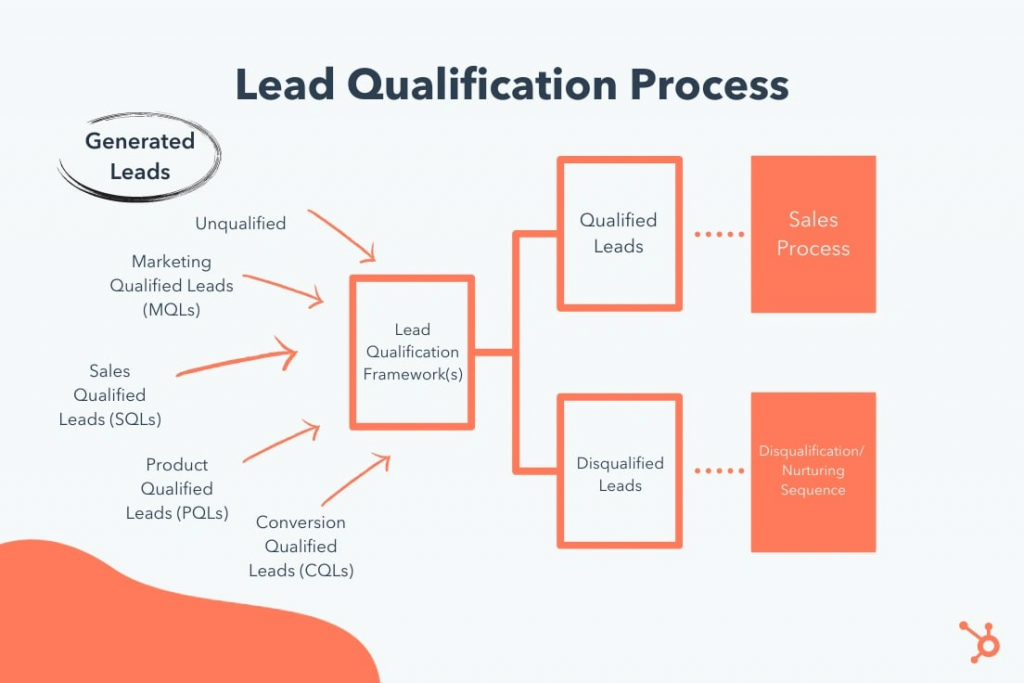
Image Source: Hubspot
Top 5 Lead Qualification Frameworks
Lead Qualification is a systematic process and there are certain frameworks that make lead qualification further effective. Let’s take a look at these.

Image Source: lucidchart.com
The BANT technique was developed at IBM and is often used by B2B businesses. It relies on four key characteristics. They are arranged in order of decreasing importance.
- Budget – What kind of purchasing budget does the client have, and does it fit the product or service on offer?
- Authority – Does the person being contacted have the authority to make the purchasing decision?
- Need – Does the product or service on offer fit the needs of the client? How urgently do they require it?
- Timeline – How ready is the client to make a purchase? Is it a priority acquisition at this time?
This is a popular alternative to BANT that was devised by InsightSquared. It gives more priority to whether the product or service on offer solves the challenges faced by the lead. The more assured a lead is that your product will solve their unique problem, the less attention they will pay to budgetary concerns. It allows businesses to focus their sales and marketing efforts on leads whose workflow has a space for their product or service. It also allows for the discarding of those leads who do not have a need for what is on offer.
MEDDIC (Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Pain Points, Champion)
MEDDIC is a comprehensive framework for lead qualification that focuses on six key elements. So, let’s break down the buying process.
First, we need to figure out what they’re really looking for. What do they want to get out of this? [Metrics]. Next, we need to find the big boss—the person who’s actually going to make the call [Economic Buyer].
Then, we need to understand what factors will sway their decision [Decision Criteria]. What are they looking for in a product or service? Once we know that, we can map out the steps they’ll take to make a choice[Decision Process].
And let’s not forget about the pain points[Pain Points]. What’s keeping them up at night? We need to show them how our solution can solve those problems.
Finally, we need to find someone inside their company who’s really excited about our product [Champion] and can champion it.
By meticulously analyzing these six dimensions, sales teams can accurately assess a lead’s potential and tailor their approach accordingly.
MEDDIC is particularly effective for complex sales cycles and high-value deals. However, it’s essential to recognize that this framework may not be optimal for all sales environments, such as high-volume, low-ticket transactions.
Developed by Hubspot, this framework encourages sales representatives to act more as advisers towards leads. They do not need to restrict themselves to just what their product or service can solve. Lead qualification questions that can be used to guide the conversation in collecting insights can include:
- What are the goals of your business?
- Do you have the needed resources to put these plans into action?
- What kinds of challenges are you facing? How are you dealing with them?
- What kind of timeline do you have for your plan?
- What kinds of consequences and implications do you anticipate with achieving your goals?
Another variation on BANT that prioritizes factors differently. Here, the top priority is given to verify if the contact has the decision-making power, with money being the last thing to consider. Notice the parallel of BANT here? This framework works best when client businesses do not have a properly established hierarchy or organization that defines roles and decision-making authority. This can be common amongst start-up companies that are still organizing themselves.
These frameworks provide a process by which to qualify leads and ascertain where the best chances of conversion lie. They provide a means by which to quantify a prospect’s behavior and information.
Let’s look at some of the factors that can be used to numerically arrive at qualified leads. This includes components from both marketing and sales lead qualification processes.
Lead Scoring Components
Different frameworks can be used to qualify leads. They all have different factors they focus on and how they prioritize. Here are some of the factors used to construct them:
- Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) – It becomes easier to figure out which leads will be more likely to convert when you have buyer profiles of your ideal customer. Strong attention should be paid to the authority of the lead. The more decision-making power they have in their organization, the stronger a lead they become.
- Company Profile – Collecting data on a prospect’s company might probably be the most important thing in B2B. It will help in figuring out if their profile matches your ICP. Their size and type of business should match up to what your business has to offer.
- Online Behaviour – How the prospect arrives on your site, the pages they visit, how many times and for how long can provide useful data points. How deep they seem to delve into the information you provide on your site can be a good indicator of their interest and intent.Also, keep an eye on their engagement. Even if they sign up for an online webinar or to be part of a mailing list, their click-through, and open rates will be more important. The same applies to their social media engagement in terms of click-through, messaging, and likes.Salespanel helps you track on-website behavior, visit duration, track custom events like webinar views and button clicks. So, if you are a user, you can most likely use this information.
- Ongoing Communication – Sales teams should update scoring with each successful and subsequent interaction or have the tool you use to score leads (Cough! Cough! Salespanel) automatically do it for you. Whenever an email is responded to promptly or a lead performs a key action, and the stronger an indication is generated that the prospect is looking to close the deal.Businesses can build their own framework for qualifying leads. Every component they identify as being relevant should be included as part of scoring. With many businesses now using some form of CRM or marketing automation system, it is becoming easier to collect and share information across the business. Having a central reservoir where lead data can be collected and assessed can help in prioritizing prospects and ensuring those with the strongest potential to convert get efficiently channeled through the sales funnel.Having a central reservoir where lead data can be collected and assessed can help in prioritizing prospects and ensuring those with the strongest potential to convert get efficiently channeled through the sales funnel.
Conclusion
Whatever lead qualification process you adopt or develop should serve two key purposes. First, it should help in identifying the best prospects amongst your leads that are worth investing more time and effort on to convert. Second, they should provide sales intelligence that allows sales teams to refine their offerings, talk to leads with high intent, and be more productive.
Most of your leads are not going to buy, and that is okay. What you need to do is to ensure that the maximum effort you put is on those deals that have a possibility of buying. If some leads are not ready yet, you will need to have a system to nurture them.
Sell more, understand your customers’ journey for free!
Sales and Marketing teams spend millions of dollars to bring visitors to your website. But do you track your customer’s journey? Do you know who buys and why?
Around 8% of your website traffic will sign up on your lead forms. What happens to the other 92% of your traffic? Can you identify your visiting accounts? Can you engage and retarget your qualified visitors even if they are not identified?


