Lead Generation Process: The Simplest Flowchart for the Most Effective Results
Updated on 7th June, 2023.
For many businesses, the process of generating leads is an essential part of the sales workflow. A lead is typically defined as a person or business who might become a customer at some point in the future.
Lead generation can be different for different businesses. However, the intent remains the same – get as many people to buy your products/services as possible. While this sounds simple, the entire process is quite cumbersome and requires too much effort. Prospects need to be nurtured at various stages to persuade them, evoke eagerness, and make them take the desired action.
In this blog, we aim to decode different aspects pertaining to lead generation, the important workflows, and the process to maximize results.
But, let’s start with the basics first
What is Lead Generation?
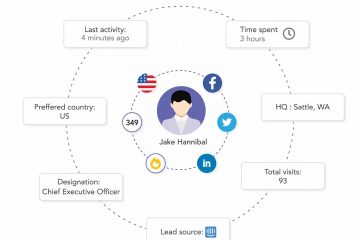
Lead generation is the process of attracting and converting potential customers into leads. These ideally include people who’ve shown interest in your product or service. It usually involves capturing their contact information for further engagement. The contact information may include their name, phone number and/or email address. For instance, a beauty brand trying to increase its customer base may run a lead generation program by offering freebies to anyone who shares details of three or more women.
Different Types Of Lead Generation Methods
One can use multiple methods and strategies to generate leads effectively and efficiently. Listed below are some such methods that you can employ.
Content Marketing: Craft and distribute relevant and valuable content via blog posts, infographics, e-books, and videos. It helps attract and engage potential leads.
Social Media Marketing: Leverage social platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Linkedin, Twitter, Youtube, and more to share relevant and topical content, engage with the potential audience base, and drive traffic to either your landing page(s) or website.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Use this marketing technique to optimize website content and structure. Use the right set of keywords to rank high on SERP. This not only helps improve your visibility but attracts traffic organically and generates potential leads.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: This is another proven way to get prospects in radar. By running paid ads on social media platforms and search engines like Google, you can display ads pertaining to your products and services, entice prospects and get them to convert into potential leads.
Email Marketing: An age-old lead generation technique, email market gives you the leverage to send personalized messages, newsletters, or promotional offers to prospects and convert them into leads.
Referral Programs: Another technique to generate leads is by encouraging existing customers to refer friends, colleagues, or family and incentivizing them for each referral lead gained.
Webinars and Events: Hosting webinars, online or offline events, workshops, or even seminars can serve as a great way to share valuable information, establish brand authority, and capture lead information.
Partnerships and Affiliates: A relatively old marketing concept, partnerships and affiliates are two of the best lead generation methods. By collaborating with businesses or affiliates alike, you can leverage their customer base and generate leads and vice versa.
The Transition of Leads through the Buying Journey
The acquisition of a new lead is just the start of the sales process. Ensuring that these prospects convert into paying customers demands building a strong, seamless and leakage proof sales funnel. That’s because each lead will go through a journey from the point of first contact with the company to the point where they make a purchase. If the funnel here is perfect, then lead to conversion rate will always be high.
The sales funnel can be broken down into four main stages:
The Lead Stage: This is the stage where a company has a database of individuals who may or may not be interested in your product/service but are worth engaging with.
The MQL Stage: Otherwise known as the Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) stage, it’s when a prospect has expressed interest in your product/service. They are considered to be more likely to buy than other leads. However, the probability remains fifty-fifty here. Ideally, these are the leads generated by the marketing team and are deemed qualified by Marketing.
The SQL Stage: The Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) stage is when a prospect is almost convinced and is considered qualified by the sales rep.
The Customer Stage: This is the last stage in a lead generation funnel where a prospect has finally made the purchase and converted into a customer.
The Importance of a Lead Generation and Processing Mechanism
As outlined above, leads are at different levels of readiness during their journey through the buying process. If you approach a lead before they are ready to buy, you are unlikely to get the response you are looking for and you may end up scaring them away. If you have a lead that is ready to buy and you leave it too late, they might end up changing their mind.
With this in mind, it’s important to process leads to help extract maximum value from them; to work with them according to where they are in the process personally.
Below is a workflow that helps outline the process of taking a raw lead through the journey to becoming a customer.
The Lead Generation Workflow
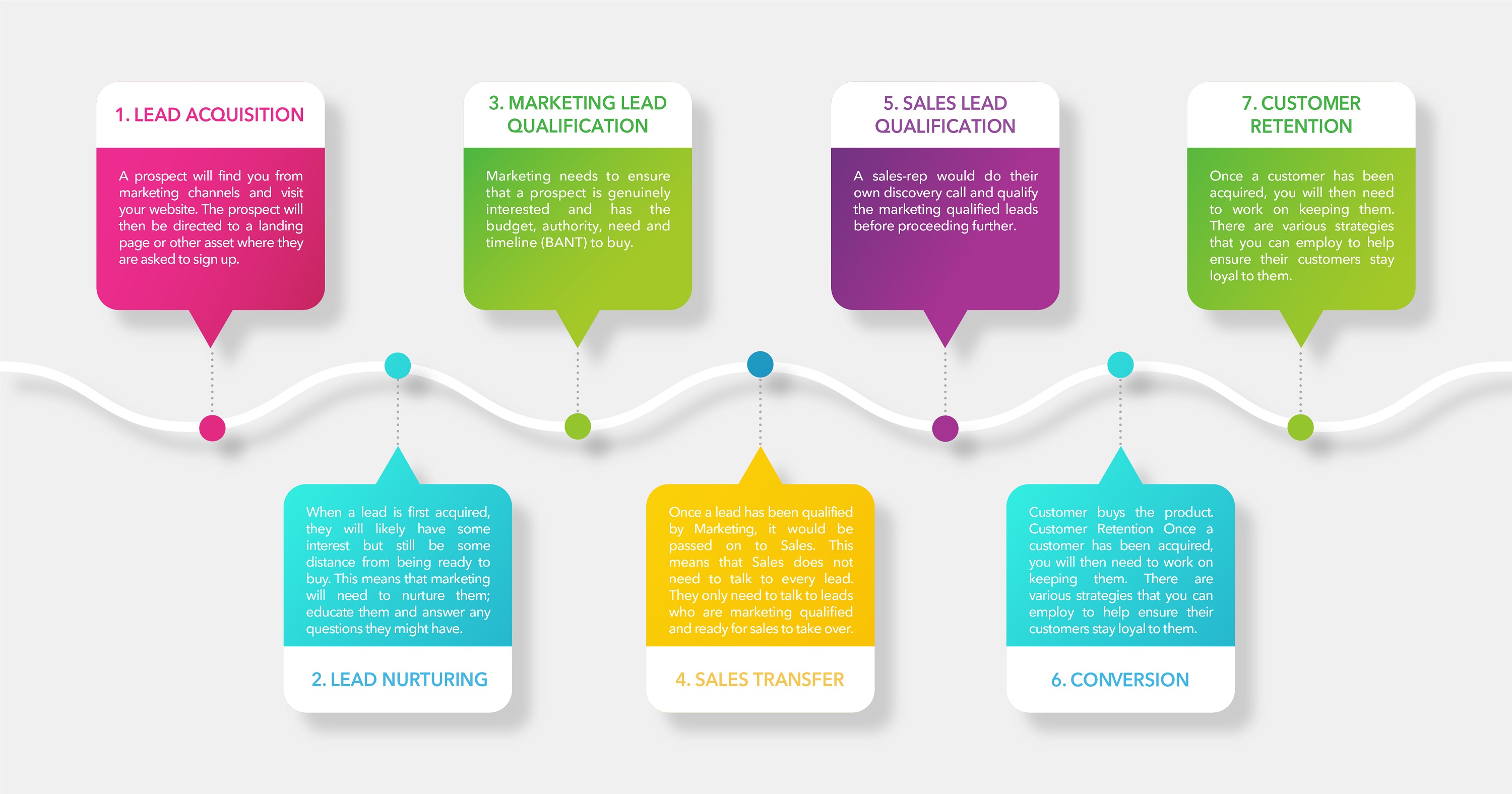
The seven stepped workflow would look something like this:
But what do each of these steps mean? Let’s take a closer look.
Lead Acquisition
There are various ways of achieving this, perhaps the most common being PPC advertising and SEO. The prospect will typically spot an ad for something they are interested in and click on it. The prospect will then be directed to a landing page or other asset where they are asked to sign up for more information on the product, news on promotions and other deals, and similar. Different methods are used to help encourage the prospect to share their personal details. One such method is known as a lead magnet which is often in the form of free content (like an eBook) – provided the prospect signs up.
Another way to acquire leads is by building a sales funnel, the organic or unpaid way. For instance, software as a service (SaaS) companies can build a SaaS sales funnel by relying less on paid ads and creating SEO-optimized and valuable content. Every content should appeal to its target audience, getting the SaaS brand in front of them at every stage of the buyer’s journey. Hence, it’s necessary to develop content that generates organic traffic and converts cold prospects to SaaS users. Once you master this strategy, you’ll attain a scalable sales funnel that converts leads exponentially.
Lead Nurturing
When a lead is first acquired, they will likely have some interest but still be some distance from being ready to buy. This means that marketing will need to nurture them; educate them and answer any questions they might have. This can be done in a variety of ways, one of the most common of which is with drip campaigns that involve sending relevant information to the prospect according to their behaviors and other factors.
Lead nurturing will also often involve remarketing. Remarketing means using ads to reach back out to prospects that have visited your site but not taken any action. It’s a great way of reminding people you’re still there. In addition, remarketing can help in lead generation and conversion. For instance, an online store can reduce shopping cart abandonment by showing the products to the user while navigating the app or sending an in-app notification or email that the products are still available and waiting for checkout.
Marketing Lead Qualification
In addition to nurturing a lead, marketing also has the task of qualifying the lead. This means ensuring the prospect is genuinely interested and almost ready to buy the product. Qualifying also means ensuring the prospect is in a position financially to make a purchase and that the contact is the person making the decision.
The importance of speaking with the decision-maker cannot be understated. If the contact is not the decision-maker then they will need to report back to the person who does make decisions. However, that person has not been through the same nurturing process that the contact has. This makes it a lot less likely a sale will be made and trying to make a sale to the wrong contact can end up with the prospect being lost altogether.
So, how can a marketer or brand connect with the right person? To reach the decision-maker, you can request your contact to arrange a virtual or face-to-face meeting or provide you with the person’s contact details. While your first contact isn’t qualified as a marketing lead, the individual can be your excellent bridge to the decision-maker, who can also serve as a referee or brand endorser.
Sales Transfer
Once a lead has been qualified by Marketing, it would be passed on to Sales. This means that Sales does not need to talk to every lead. They only need to talk to leads who are marketing qualified and ready for sales to take over. Marketing can use a tool like Salespanel to qualify leads using segmentation and lead scoring and automatically transfer them to sales when leads are marketing qualified.
Sales Lead Qualification
Although marketing is expected to qualify a lead, sales will also often perform their own qualification check. This might involve somebody from sales giving the prospect a call to ask them more questions and evaluate their readiness to make a purchase. The process also helps to prep the prospect further for a sale to help ensure they are ready when an offer is made.
If the lead is not fully qualified yet then it does not necessarily mean the prospect is lost. Sales can find out the reason why the prospect is not ready and, if needed, pass them back to marketing who can get back to the task of nurturing the prospect until they are ready to buy.
Conversion
Of course, the ultimate task for sales is to convert the lead into a customer. Or, in other words, compel them to buy the product. This will often mean negotiating with the client regarding price and terms and conditions to try and come to an agreement. It’s also often important for the sales department to maintain a good relationship with the customer because there will often be other sales opportunities further along the line, such as other products, and upgrades to products the customer has already purchased.
Customer Retention
Once a customer has been acquired, you will then need to work on keeping them. There are various strategies that you can employ to help ensure their customers stay loyal to them.
- Customer Services: Things will occasionally go wrong – it’s a part of life. What really matters is how a company deals with problems when they do occur and how they put things right for their customers. A good customer service department will help to overcome any issues that do occur, helping to keep the customer happy. In a sense, having problems arise can even work in the company’s favor as it’s an opportunity for the company to show they do have their customer’s best interests at heart.
- Loyalty Rewards: Loyalty reward systems are very popular. They help companies let their customers know they are appreciated, encouraging the customer to stick around for longer. Loyalty rewards are also great for driving extra revenue as they encourage people to take up deals and make purchases that they might otherwise not have taken.
- Request Feedback: Feedback, good or bad, can be instrumental in helping you to keep your customers on board. For one, thing, people appreciate being given the opportunity to voice their opinion. For another, the feedback you receive can help you to maintain high standards and continue delivering what the customers want. Try not to reject negative feedback. If anything you should embrace it. See it as your customers telling you how to deliver quality service and product, helping you to keep them for long into the future.
Conclusion
Generating revenue involves so much more than just telling people you have something and waiting for them to buy. Instead, it involves whole processes within processes, each of which leads up to the next process and is part of an overall sales and marketing campaign. The process is also not over when the customer buys something. Rather, it is simply the beginning of another process that can go on throughout the customer lifecycle.
Above is a brief outline of a typical flowchart of these processes and how they tie in with each other. It shows how different departments will need to work with each other and how those at the very beginning of the process are essential for those at the end. If you were to follow this outline as a guide then you are well on your way to generating more revenue in the short term and the long term.
Recommended Reading:
B2B Lead Generation Strategies and Tools for 2021
Sell more, understand your customers’ journey for free!
Sales and Marketing teams spend millions of dollars to bring visitors to your website. But do you track your customer’s journey? Do you know who buys and why?
Around 8% of your website traffic will sign up on your lead forms. What happens to the other 92% of your traffic? Can you identify your visiting accounts? Can you engage and retarget your qualified visitors even if they are not identified?