Lead Scoring Best Practices: A Definitive Guide to Converting High-Intent Buyers
When digital marketing first began, lead qualification was more of a more art than a science, relying on intuition and manual list-scrubbing. Many leads were unqualified, wasting up to 50% of their time on unproductive prospecting. This wasted time could have been avoided by focusing more on the science of lead qualification. However, times have changed. B2B buyers move through a large part of their journey on their own. When they do decide to connect with a salesperson, they usually leave plenty of digital footprints. The real challenge now is no longer finding leads but rather scientifically identifying the truly sales-ready prospects within the sea of digital unwanted noise.

This is where modern lead scoring diverts from its simple beginnings. It is no longer just a static, simple points system; it has become a dynamic, predictive system designed to create a powerful cohesion between marketing and sales. Its aim is to save time and resources, impact revenue growth, and close more deals with effective models that increase close rates by as much as 30%. This article aims to provide a definitive guide on lead scoring best practices and moves past generic advice. As with all things, the goal is precision; lead management should shift from being a reactive system to a predictable growth machine. There will be technical frameworks, practical examples, and strategic insights that will help in the identification of high-intent buyers with scientific accuracy.
1. Define Clear Lead Scoring Criteria and Point Values
Well-defined criteria and a logical point system are essential for any effective lead scoring model. Assigning numerical values to a lead’s attributes and actions, reflecting potential value and sales-readiness. It turns subjective scoring into a more analytical data-driven approach. All scoring should be data-driven and not subjective.
Next is uncovering the indicators that signal a high-quality lead for your business. These indicators are categorised into explicit data (demographics and firmographics) and implicit data (behaviors). A comprehensive lead scoring approach incorporates both a holistic view of each prospect. A systematic approach ensures that the sales team consistently receives leads that are interested and a good fit for your product or service. At Salespanel, we appreciate the philosophy of unifying explicit and implicit data to lead intelligent lead qualification. This is the cornerstone of intelligent lead qualification

Actionable Implementation Steps
Constructing a robust scoring matrix requires a look at historical data. What are the traits of customers who have closed successfully? What are the traits of customers who have not converted? The data comparison will surface your most predictive criteria.
Firmographic & Demographic Scoring:
Points can be assigned according to the explicit data a lead has provided. This data will qualify their fit.
For example, B2B enterprise sales to B2B software companies are assigned higher scores based on lead job titles and company size.
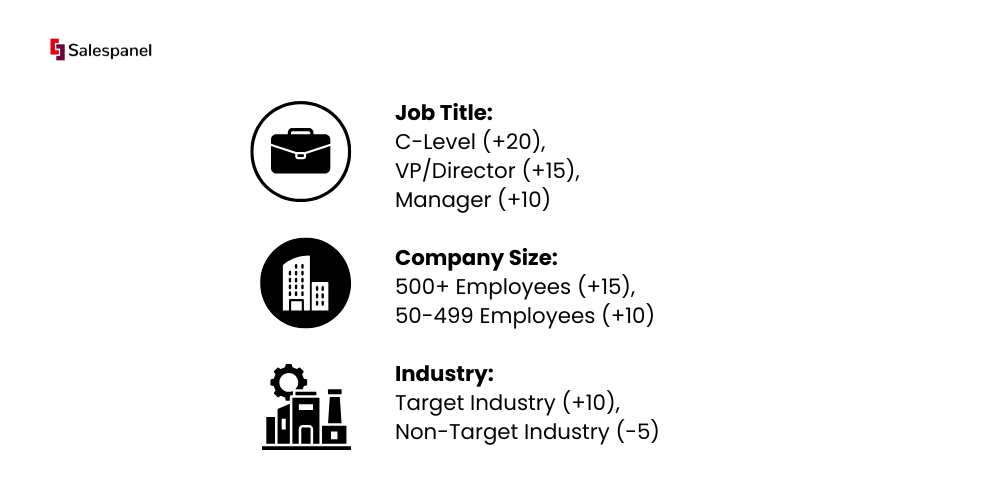
Behavioral Scoring: Award points for implicit signals that indicate interest and intent.
Practical Example: A prospect’s digital body language reveals their buying intent. High-value actions receive more points.
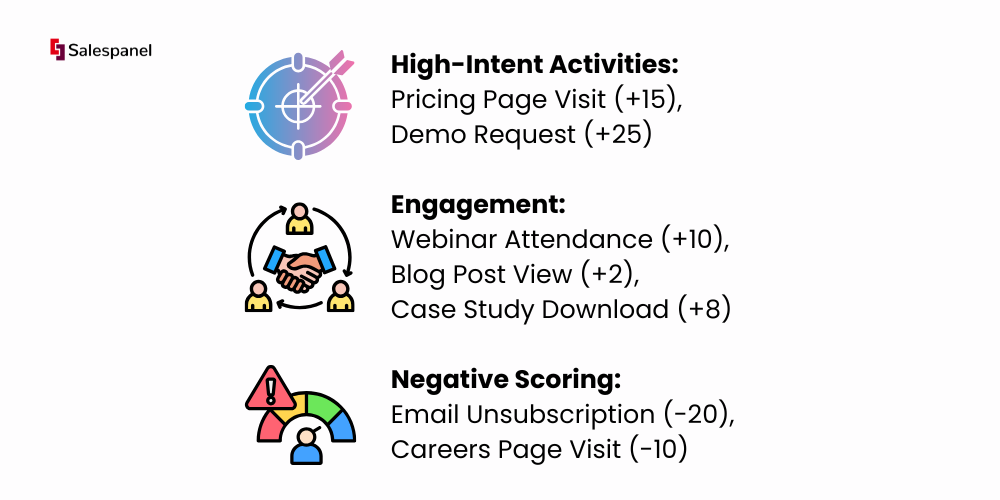
Establishing clear thresholds is key. For instance, a lead with 50 points could be considered a Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) to be nurtured, while a score of 100+ identifies them as a Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) ready for immediate sales outreach.
2. Implement Demographic and Firmographic Scoring
Behavioral data reveals what a potential customer wants, but demographic and firmographic data show whether they are a good fit. This scoring method looks specifically at how prospects provide explicit information and how information might be augmented from other sources. This involves systematically grading, on how close they are to your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP), so that your sales team focuses on leads that can actually buy your product.

For B2B organisations, this is the foundational layer of lead scoring best practices. When you focus your efforts on the right industries, company sizes, and job functions, you help your sales team avoid stalls from poorly aligned prospects. The right focus helps you qualify leads before they ever take a high-intent action, so you can create a more efficient and predictable pipeline from the very beginning. Platforms like Salespanel are excellent for capturing and enriching firmographic data, which helps convert anonymous visitors into qualified company profiles.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Analyse your customer base to identify common attributes among your most successful accounts. Data enrichment tools help fill missing profile details for accuracy.
Positive Fit-Based Scoring: Give points to leads that correspond to your ICP characteristics. This allows you to prioritise your most valuable potential customers.
Practical Example: A Cybersecurity Company that targets financial institutions would score leads as follows:
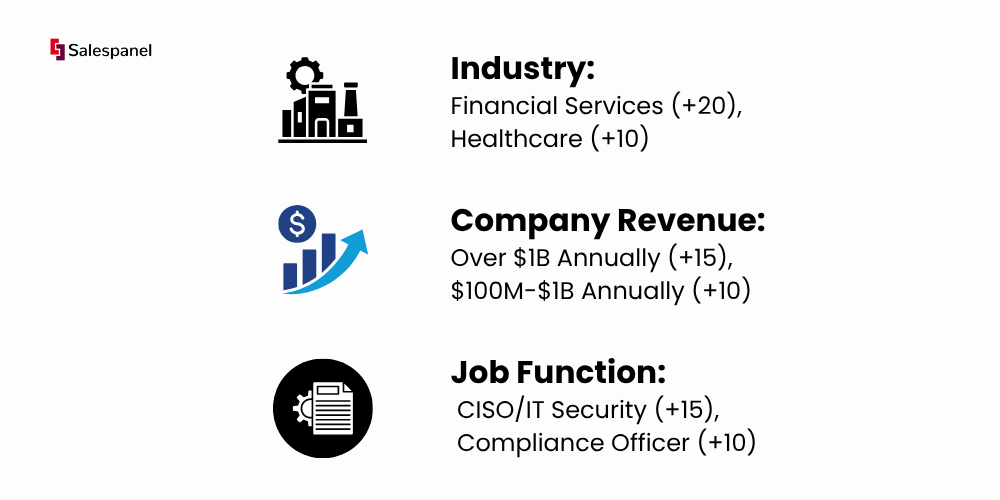
Negative Fit-Based Scoring: Apply negative points to disqualify leads outside your target market. This keeps your sales pipeline clean and focused.
Here is a practical example of filtering out non-buyers.

Combining positive and negative fit scoring creates a powerful filter. A lead from a target industry with a decision-making title rises to the top, while a student or competitor researching your company is deprioritised—keeping your team focused solely on high-potential opportunities.
3. Track and Score Behavioral Engagement
Salespanel empowers you to assess genuine interest with the help of behavioral data. With Salespanel insights, you score a prospect’s interactions across digital touchpoints—websites, emails, and content downloads. Monitoring these implicit signals is essential to understanding purchasing intent and pinpointing a prospect’s position in their buying journey.
This dynamic scoring methodology moves beyond static profile attributes to capture real-time engagement. It enables clear differentiation between a casual browser and a serious buyer. By systematically scoring actions, you accelerate funnel progression with greater accuracy. At Salespanel, we emphasise capturing first-party behavioral data to build the most accurate picture of buyer intent. This is one of the most effective lead scoring best practices for modern B2B teams.

Actionable Implementation Steps
Scoring behavior that you want to score begins with mapping out key actions that indicate movement through your sales funnel. While all behaviors can give you clues, not all have the same value, like a visit to your pricing page holds more weight than a page visit to your blog. Advanced visitor tracking systems can perform this for you.
Weight High-Intent Actions Heavily: Assign higher point values to actions that show purchase decisiveness. This is your prime area of focus.
Practical Example: An e-commerce platform provider tracks these user actions to gauge seriousness:
| Intent Signal Type | Example Actions | Points Assigned |
|---|---|---|
| High-Intent Pages | Pricing Page Visit, Demo Request, Contact Us Form Submission | +15, +30, +25 |
| High-Value Content | Case Study Download, ROI Calculator Use | +10, +12 |
| Low-Intent Actions | Blog Post View, Social Media Click | +3, +1 |
Consider Engagement Recency and Frequency: A lead that frequently hops onto your site within a week is more engaged than one that visited three months ago for the first time.
Recency: Award bonus points with extra points for actions completed in the last week.
Frequency: Control points for repetitive visits to important pages (for example, three visits to a page that details a certain product feature) within a time frame as this page indicates focused interest.
Score Decay: Implement a system where points expire over time, creating a more accurate assessment of the lead. For example, Salespanel accounts for score decay, a crucial aspect in your sales pipeline to manage focus on a lead who was hot 3 months ago but has since cooled.
4. Create Negative Scoring Rules
Negative scoring is systematically deducting points or actions, indicating a disqualified, unqualified, or uninterested lead. Just like mathematically negative scoring constructs a picture of a lead potential, Negative scoring is essential for building a picture of a lead potential. Acts as a filtration system while blocking the sales pipeline from becoming clogged.
When a lead checking out the pricing page is awarded 15 points, a “Student” job title is likely not a viable prospect with a -50 point total. This negative scoring leads to being mistakenly flagged as sales-ready, saving time and lead resources. Purifies your lead pool.
Rules must be devised to score those unqualified, unengaged leads or deals.
Firmographic & Demographic Negative Scoring: For data that does not fit the ideal customer profile, negatively score.
Practical Example: For marketing agencies focusing on mid-market clients, the criteria would be:
- Invalid Data: Personal, non-work-related emails (like gmail.com, yahoo.com, etc.) (-15)
- Disqualifying Job Titles: Job titles such as “Student,” “Intern,” or “Unemployed” (-50)
- Competitors: Email domain tied to a competitor (-100 or disqualified)
- Location: Country or region that you do not service (-30)
Behavioral Negative Scoring: Helps to refine where a lead might not fit or where a lead might not be interested.
Practical Example: Assessing disengagement signals in your marketing helps to keep the pipeline clean.
| Action Type | Example Actions | Points Deducted |
|---|---|---|
| Disengagement | Unsubscribing from marketing emails | -25 |
| Low-Fit Interest | Overly focused on the “Careers” or “Jobs” page | -10 |
| Inactivity | No engagement (email opens, site visits) in over 90 days | -20 |
Focus first on clear disqualifiers, such as competitor domains or student emails. These criteria should regularly help cleanse the sales pipeline.
5. Establish Lead Scoring Thresholds and Handoff Processes
A lead scoring model is only as effective as the actions it triggers. Establishing clear thresholds and deciding which level a lead will transition to next. For e.g., A generic contact moving from a Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) to a Sales Qualified Lead (SQL). This leads to a predictable, automated, and systematic process of handoff from the marketing team to the sales team. This is a cornerstone in revenue operations today.
Without defined thresholds, even the most precise scoring system will fail to deliver value. Leads will score points, and there will be no end result; this will lead to inaction. This ensures sales to engage leads when they are at the peak of fit and interest, avoiding premature outreach and delayed follow-up. This effectively ties the marketing team’s lead generation to the sales team’s conversion activities, unified and efficient revenue engine.
This simple workflow visualises how a lead progresses through the qualification stages as their score increases. The sales team is only engaged when the final score threshold is reached and a handoff is triggered. This makes it easy for the sales team to follow up with leads and close more deals.
The above chart illustrates how having preset point values for MQL and SQL status unambiguous pathway for leads to progress and for timely sales intervention.
Actionable Implementation Steps
To implement this best practice, you need to determine what each threshold means and what the exact process will be afterwards. This involves defining MQL and SQL, requires close collaboration with sales, and establishes clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
Define Threshold Tiers: Create distinct levels. This makes certain that each lead is handled appropriately according to its score.
Practical Example: The following example comes from a typical B2B SaaS company.
- Nurture (1-49 points): The lead is not ready for sales and needs to stay in the marketing automation nurture campaigns.
- MQL (50-74 points): The lead has met marketing’s qualification criteria and is sent to an SDR for further evaluation.
- SQL (75+ points): The lead is ready for sales as they take high-value actions, and they fit the criteria. Assign them to an Account Executive for immediate outreach.
Automate the Handoff: Use a platform for your marketing automation tools, or your CRM, with workflows that will automatically update a lead’s status and assign ownership when that lead’s threshold is met.
Practical Example: Take, for instance, when a lead’s score reaches 75, a workflow in your platform assigns the lead to the appropriate sales rep within your CRM and creates a task for a follow-up within 24 hours.
Establish Clear SLAs: Document the agreed-upon rules for engagement for an SLA. An SLA dictates that all SQLs are to be contacted by sales within a specific timeframe, ensuring no qualified lead is neglected. This accountability is critical for maximising conversion rates from your lead scoring.
6. Regularly Review and Optimise Scoring Models
A lead scoring model is set and forget it. Regularly reviewing and optimising includes market, customer, and internal business goal changes. This process entails systematic analysis through closed-loop reporting and scoring leads to assessing the model against real sales results. Every model needs regular performance assessments, and every business must meet its changing business goals.

The model must be kept predictive by evaluating performance against score expectations. The iterative approach through multiple states of lead scoring maturity to create intelligent scoring. Commitment to data-driven refinement. This consistently delivers high-quality, sales-ready leads, while every other lead will be systematically removed from the model for the greatest ROI.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Performance data guides model changes to construct a feedback loop from marketing to sales. These scoring results lead that reliably convert approximately 98% of the time. Conversion changes lead the predictive scoring model to close the intent of the customer with a perfect score, while the marketing score lowers by closing leads to are predicted.
Analyse Lead-to-Customer Conversion Rates:
It’s time to stop looking only at MQLs and SQLs. What really matters is which leads are actually turning into paying customers.
High-Scoring Leads, No Conversion: Dig deeper into why you aren’t closing leads with high scores (like 100+). Are they a poor fit, or is there something wrong with your sales process? Maybe signing up for a high-point activity, like a webinar, is less indicative of purchase intent than you thought.
Low-Scoring Leads, High Conversion: Find out which customers converted that had low scores and what your predictive attributes and behaviours should have included did your model missed?
Practical Example: Imagine a SaaS company that repeatedly sees visits to its API documentation. The visits are initially unscored, but become a major buying signal from a technical user who will become a champion for the SaaS company. That would likely lead to the company gaining points for that behaviour, which is a positive action.
Schedule and Document Regular Reviews: Prioritising the scheduled documentation of your model optimisations regarding process analytics will lead to smoother improvements.
Quarterly Reviews: Format a routine with both sales and marketing stakeholders to analyze your performance data and brainstorm prospective model adjustments.
Change Log: It is important to have a record of every modification to the scoring model along with the date of the change, the change’s implications, and the change’s rationale.
A/B Test Changes: Test major adjustments to scoring on a small slice of new leads to see how they affect lead quality without altering the whole pipeline.
7. Integrate Lead Scoring with CRM and Sales Process
The application of a lead scoring model determines its worth. Integrating the scoring systems directly into Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems is the critical step that converts theoretical scores into actionable sales intelligence. This practice prevents the rich data gathered by marketing from not lost in translation and places it directly into the hands of the sales team, right within their daily workflow. This is a great operationalise your data. It makes them central and visible to every lead record.

Embedding lead scores bridges the classic divide between marketing and sales with real-time data on customer engagement levels. Seamless connection and real-time alerts on high-scoring leads streamline outreach, greatly enhancing efficiency and profitability. Unified customer profiles from marketing and sales activities provide a comprehensive view of the customer’s journey, making this one of the most impactful best practices in lead scoring. Salespanel syncs lead scores and behavioural journey data points to your favourite CRM in real-time.
Actionable Implementation Steps
Effectively merging with your sales process seamlessly would require direct focus on their accessibility, understandability, and automation in your CRM. This is to eliminate friction and allow sales teams to empower reps to act on scoring insights without leaving their primary platform.
Ensure Data Visibility and Context: The lead score should be one of the key pieces of information on a contact or lead record in your CRM.
Practical Example (Salesforce): Go to ‘lead’ contacts and drag the ‘score’ field into the primary contact layout. Then, go to ‘Components’ and create a ‘Recent Activity’ component that shows the top 5 behaviours contributing to the score (e.g., ‘Pricing Page Visited’, ‘Case Study Downloaded’).
Practical Example (HubSpot): In contact views, use the score property. Then, create reports that segment contacts by score, so they can easily be prioritised.
Automate Lead Routing and Sales Actions: Automated workflows can turn scores into actions that speed up the sales cycle.
Automated Assignment: Create a rule to automatically assign leads with scores above 100 to senior sales representatives.
Task Creation: When a lead’s score surpasses the SQL threshold, trigger an automated task to the sales rep that says, “Call within 24 hours”.
Real-Time Alerts: If a lead’s score increases by 20 points or more or they view the pricing page, set up a Slack or email notification to the account owner.
The final, crucial step is training. Your sales team needs to understand what the scores mean and how to tailor conversations accordingly. For instance, a rep who recognises a lead downloaded a particular case study will start the conversation with a much more relevant and powerful opening.
8. Implement Multi-Touch Attribution in Scoring
Defining a lead’s score based solely on one interaction, such as a first or last touchpoint, gives an incomplete and often misleading picture. A more sophisticated lead scoring best practice is to implement multi-touch attribution. This recognises the cumulative impact of every interaction over the course of the B2B buyer’s journey. This methodology realises that prospects engage with numerous channels and pieces of content over a period of time, facilitating a far more accurate measure of interest and intent.

This approach advances beyond simplistic scoring models by attributing value to every touchpoint that influences a prospect’s path to conversion. Unlike other approaches, this practice recognises the interdependence of a prospect attending a webinar three months prior, downloading a white paper last week, and visiting the pricing page today. By weaving these interactions together, a dynamic score that reflects the entire relationship is built, and sales can operate on the most holistic understanding of engagement history rather than vague bits of data from a single moment.
Actionable Implementation Steps
By establishing and implementing multi-touch attribution, the tracking and weighing of interactions within the entire automated customer journey can be achieved. This will, of course, require robust tracking capabilities and a clear strategy for assigning value to each engagement touchpoint.
Define Key Touchpoint Sequences: Find patterns for sequences of touchpoints for high-value clients where touchpoints are converted. If a prospect attends a webinar, then downloads a related case study, and ultimately requests a demo, they exhibit a distinct pattern of increasing intent.
Practical Example (SaaS): A software company could award a score of +30 to leads who attend a product webinar, go to the integration page, and then view the pricing page within two weeks. This acknowledges an important series of high-intent activities.
Practical Example (Consulting): A firm might increase the score for an account when several people from the same company download a research report and register for an executive roundtable.
Apply a Time-Decay Model: Not all interactions are equal, and more recent activity is more indicative of intent. A time-decay model places greater emphasis on recent interactions and time; touchpoints, and scores will remain relevant.
Practical Example: A lead’s score is adjusted based on when an action occurred.

Leverage Attribution Tools: For starters, look at the attribution models within your marketing automation or CRM system. For more advanced analysis, explore specialised tools that connect complex user journeys and offer insights into which channels and campaigns bring in the most qualified leads.
Lead Scoring Best Practices Comparison
| Lead Scoring Method | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Define Clear Lead Scoring Criteria and Point Values | Medium – requires design of scoring matrix | Moderate – data analysis, cross-team input | Consistent lead evaluation, better prioritisation | General lead qualification across buyer journeys | Aligns marketing and sales, improves conversion |
| Implement Demographic and Firmographic Scoring | Low to Medium – focuses on static data | Moderate – CRM data, enrichment tools | Quickly identifies ideal profile leads | Early-stage qualification, account-based marketing | Filters unqualified prospects early |
| Track and Score Behavioural Engagement | High – need tracking infrastructure | High – marketing automation, analytics | Real-time insight into buying intent | Behaviour-driven lead nurturing and prioritisation | Detects true engagement, enables personal follow-up |
| Create Negative Scoring Rules | Low to Medium – define disqualifiers | Low to Moderate – requires data hygiene | Reduces poor quality leads in the pipeline | Prevent sales waste, data quality maintenance | Saves time, improves lead database accuracy |
| Establish Lead Scoring Thresholds and Handoff Processes | Medium – involves process automation | Moderate – CRM automation and coordination | Streamlined lead handoff, timely sales action | Marketing to sales lead transition management | Prevents premature engagement, automates workflows |
| Regularly Review and Optimise Scoring Models | Medium to High – ongoing analysis and testing | Moderate to High – analytics resources | Improved accuracy and conversion over time | Dynamic markets, evolving buyer behaviours | Continuous improvement, better alignment with results |
| Integrate Lead Scoring with CRM and Sales Process | Medium to High – technical integration | High – API, CRM customisation, training | Actionable insights integrated into the sales workflow | Sales teams needing real-time lead intelligence | Automates lead routing, boosts sales productivity |
| Implement Multi-Touch Attribution in Scoring | High – complex tracking and modelling | High – advanced tools and data science | Holistic view of buyer journey and intent | Complex B2B cycles, account-based marketing | More accurate, accounts for multiple interactions |
Your Blueprint for Intelligent Lead Qualification

Transforming your scattered lead data into a predictable engine stream starts with intelligent qualification. We’ve outlined the key pillars of contemporary B2B lead scoring, emphasising the transition from simplistic point systems to developing a more dynamic, responsive framework. Implementing these lead scoring best practices isn’t about going through the motions; it’s a tactical shift concerning the collaboration between your marketing and sales teams to find and engage those prospects with the greatest potential. One idea captures the spirit of these strategies best: intelligent lead scoring must function as a living system with live data and market feedback. It must adapt and shift to your current business objectives.
Constructing your system around a holistic model that integrates demographic, firmographic, and nuanced behavioural signals means lead scoring will articulate sales readiness. This is no longer a theoretical approach. It is the practical application of data to solve the fundamental problem of sales resource allocation to the most likely prospects.
Key Takeaways for Immediate Action
Let’s outline the most essential elements of this blueprint. Your immediate next steps should prioritise the establishment of a solid and adaptable foundation. This is your definitive plan.

Alignment is Non-Negotiable:
The most advanced scoring algorithm will fail without marketing and sales alignment on the definition of a “sales-qualified lead” (SQL). Your first step is always to initiate this dialogue and document the agreed-upon definition.
Behavior Tells the Story:
Demographics tell you who the lead is, but behavior shows you their intent. You want to track and score aggressive, high-value actions, especially those that clearest signal of buying intent, like visiting pricing pages and requesting demos.
Negative Scoring is a Filter, Not a Punishment:
You want to implement negative scoring. It is a powerful lead scoring best practice and will help you maintain a clean pipeline. It will filter out poorly matched leads, students, and competitors so that your sales team can channel their efforts to where they’re most needed.
The Model is Never “Done”:
You want to treat your lead scoring model like a product, not a project. Regular reviews, scoring conversion analysis, and sales-need-based model optimisations are key to long-term success.
From Blueprint to Reality

A thoughtfully designed lead-scoring system is like the central nervous system. It ensures all the revenue-generating leads are optimised and prioritised through smart, metric, and value-loaded automation. It bridges the gap between the broad-net casting of marketing and the spear-fishing of sales to form a scalable and streamlined conversion funnel.
With this system, sales teams gain the ability to focus, and the context provided is critical in their conversations. With a high-scoring lead, sales can visualise a story of engagement and interest signal, a perfect fit, and a validated signal of interest, all in story form. This is the ultimate target: To turn disparate data into a clear, actionable sales plan, creating reliable pathways to revenue.
We hope you liked our coverage on lead scoring-related best practices. If you have any feedback or if you want to add anything to the article, please reach out through our support channel.
Sell more, understand your customers’ journey for free!
Sales and Marketing teams spend millions of dollars to bring visitors to your website. But do you track your customer’s journey? Do you know who buys and why?
Around 8% of your website traffic will sign up on your lead forms. What happens to the other 92% of your traffic? Can you identify your visiting accounts? Can you engage and retarget your qualified visitors even if they are not identified?


